What is Exception?
When an error occurred in a program during execution java will throw an error message which is technically call Exception(throw an error). As a result test case gets failed in Selenium and stopped to execute.
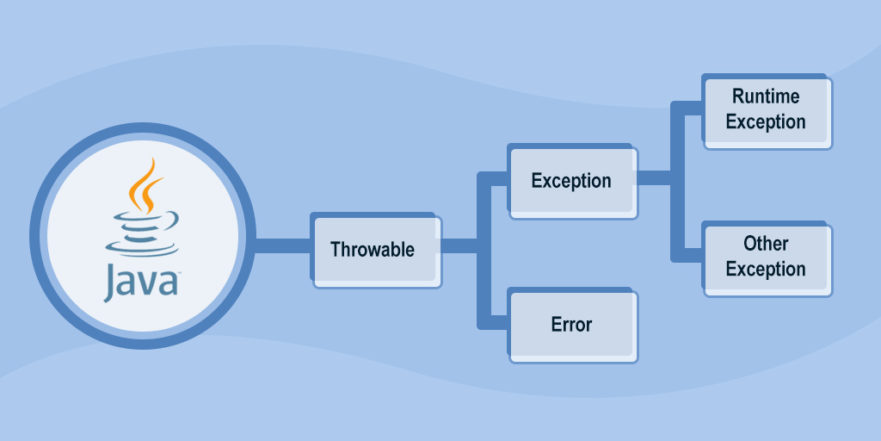
Type of Exception in Java?
Throwable is a super class in Java. It has 2 sub class as Error & Exception.

What is Exception Handling?
-Handling any unexpected programming behavior during run time is called exception handling.
-In java there is an exception handling mechanism which is applicable in Selenium. According to that, if a known method gets failed at runtime at certain condition, then we can handle that exception using the mechanism is known as Try/Catch block.
Syntax try/catch:
try{
//Block of code to try/test the error
}
catch (Exception e){
//Block of code to handle errors.
}
Example:
public class ExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
System.out.println(a[10]);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("Something went wrong in try block. I am in catch block. The Exception is below:");
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Message is:" + e.getMessage());
System.out.println("Cause is:" + e.getCause());
}
finally {
System.out.println("This is finally block!");
}
}
}
Notes:
- Throwable is a super class. It has 2 sub class as Error & Exception.
- try :block of code to try error
- catch: block of code to handle error
- finally: block of code will execute after try-catch regardless of the result. So, finally code will execute always either try/catch block works or not.